TOTP Definitions and Key Concepts
Terms used with TOTP
TOTP/OTP
Time-based One-Time Password as defined in RFC 6238. VTScada's OTPs are numeric.
Authentication
Authentication is the process of verifying that a user is who they claim to be. TOTP authentication proves the user by requiring them to possess a registered and (presumably) secured device in order to provide a time-sensitive one-time password to log in.
Authenticator
A tool or application that verifies the user is who they claim to be. Two popular authenticators are Microsoft Authenticator and Google Authenticator.
Prover
Prover is the term used in RFC 6238 for what is often called the authenticator. You made need to select the prover from a droplist if you have registered multiple provers.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
A security method that requires users to provide two independent forms of verification to prove their identity.
Multifactor Authentication (MFA)
A security method that requires two or more independent forms of verification to prove identity.
Key Concepts - TOTP Essentials
TOTP makes use of a simple algorithm to enable two isolated machines (like a cell phone and a workstation) to independently generate identical passcodes.
By going through the registration process, a secret known by VTScada is shared with the registered device. Each generated secret is random and time sensitive. VTScada only displays the secret at registration time for 90 seconds. After the secret is shared, the user must enter a time-sensitive one-time passcode from the device they're registering. This guarantees that the secret was successfully shared.
At this point, the VTScada application and the registered device share a secret. The secret is combined with the current time and both machines use the same secure hashing method to independently produce an identical 6-digit time-sensitive one-time passcode.
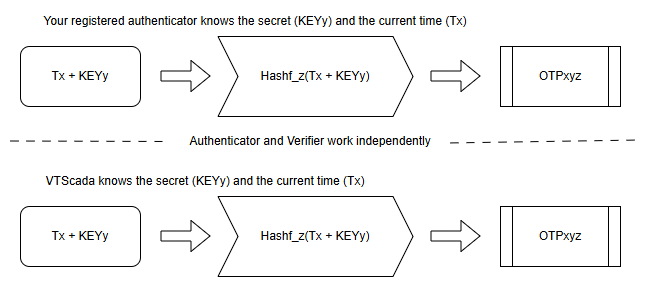
Using the same secret, same time and same secure hash method, your device and VTScada expect matching passcodes.
GPS controlled network time server
In an air-gapped system, for accurate clock synchronization you can use a GPS controlled network time server. This is a dedicated server that receives precise time data from GPS satellites without the need for external network access. GPS controlled network time servers can be purchased inexpensively from specialist retailers.
