TI505 Driver Addressing
VTScada provides an Address Select dialog (Address Assist / Address Select) to help you build I/O addresses that work with your TI505 Device driver.
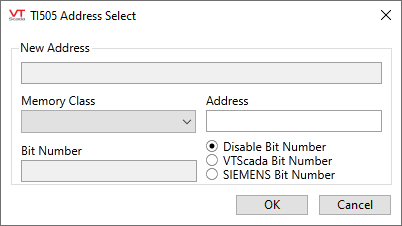
Configuring an analog tag to use a TI505 address.
TI505 addresses take the form, MemoryClass followed by an Address number. For example, WX100 for Word Input at address 100.
Memory Class
Available memory classes include:
| Memory Class Name | Memory Class |
|---|---|
| V Memory | V |
| Memory | K |
| Discrete Input Packed | X |
| Discrete Output Packed | Y |
| Control Register Packed | C |
| Word Input | WX |
| Word Output |
WY |
| Timer/Counter Preset | TCP |
| Timer/Counter Current | TCC |
| Drum Step Preset | DSP |
| Drum Step Current | DSC |
| Drum Count Preset | DCP |
| System Status Word | STW |
| Drum Current Word | DCC |
PID Loop Variables
Support is provided for the following:
- LKC. (dot variable)
- LPV. (dot variable)
- LSP. (dot variable)
- LMN. (dot variable)
- LERR. (dot variable)
- LMX. (dot variable)
- LPV
- LMN
- LSP
- LERR
Bit Number
A bit number can be enabled for reading inputs, but do not use for writing.
Note that the maker of the TI505 device uses a very different bit numbering convention for its hardware than the VTScada standard:
16-bit data is numbered 1..16 instead of 0..15.
Bit 1 is the most-significant bit, and Bit 16 is the least significant bit32-bit data is numbered 1..32.
Bit 1 is the most-significant bit of the most-significant byte.
To accommodate this, I/O addresses for the TI505 accept both bit conventions:
- Traditional VTScada bit numbers are preceded by the '/' character.
Example: V200/0- SIEMENS bit numbers are preceded by the "." character.
Example: V200.16
The Address Assist module has been modified to account for this. The "Enable Bit Number" option is now a radio button control that offers three options:
- Disable Bit Number
- VTScada Bit Number
- SIEMENS Bit Number
